Summer brings increase in Legionnaires’ disease
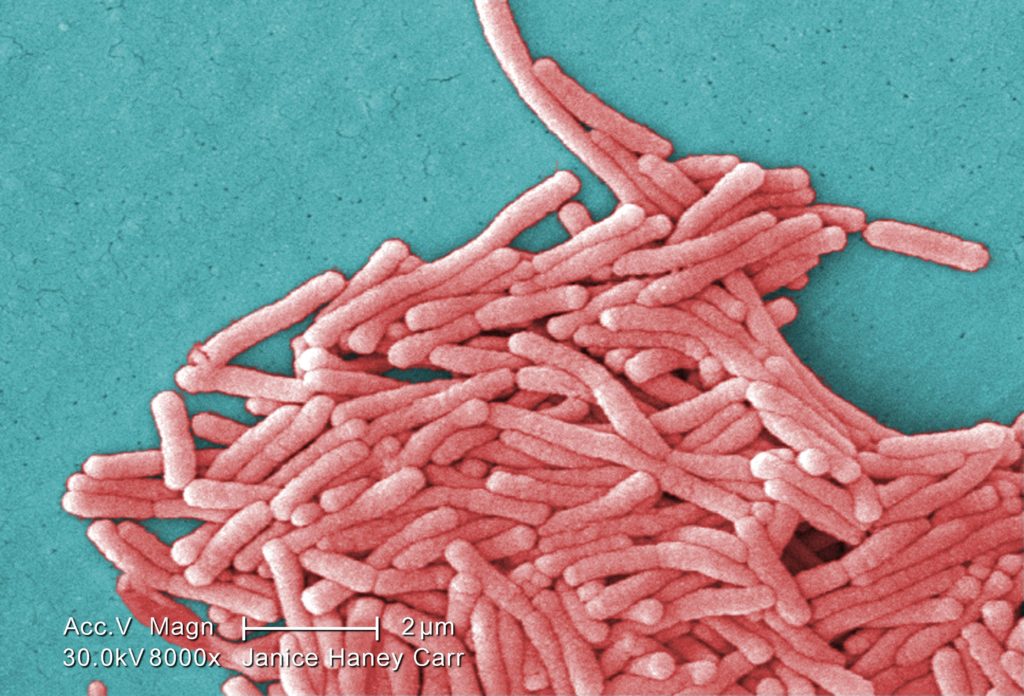
2009 Margaret Williams, PhD; Claressa Lucas, PhD;Tatiana Travis, BS Under a moderately-high magnification of 8000X, this colorized scanning electron micrograph (SEM) depicted a large grouping of Gram-negative Legionella pneumophila bacteria. Please see PHIL 11092 through 11154 for additional SEMs of these organisms, specifically PHIL 11149 for a black and white version of this image. Of particular importance, is the presence of polar flagella, and pili, or long streamers, which due to their fragile nature, in some of these views seem to be dissociated from any of the bacteria. Youll note that a number of these bacteria seem to display an elongated-rod morphology. L. pneumophila are known to most frequently exhibit this configuration when grown in broth, however, they can also elongate when plate-grown cells age, as it was in this case, especially when theyve been refrigerated. The usual L. pneumophila morphology consists of stout, fat bacilli, which is the case for the vast majority of the organisms depicted here. These bacteria originated on a 1 week-old culture plate (+/- 1 day), which had incubated a single colony, at 37?C upon a buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) medium with no antibiotics.